11
2025
-
06
The Environmental Benefits of Using Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
The Environmental Benefits of Using Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics have emerged as a sustainable solution within the textile industry, bridging the gap between functionality and ecological responsibility. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, industries are increasingly seeking alternatives that minimize carbon footprints and promote sustaina
The Environmental Benefits of Using Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics have emerged as a sustainable solution within the textile industry, bridging the gap between functionality and ecological responsibility. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, industries are increasingly seeking alternatives that minimize carbon footprints and promote sustainability. This comprehensive article delves into the numerous environmental benefits of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, outlining their contributions to eco-friendliness and sustainability.
Understanding Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
Before we explore the environmental benefits, it is essential to understand what polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are. These materials are created from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer, through a process that forms fibers without weaving them together. This method results in a versatile fabric with a wide range of applications, from personal protective equipment to home textiles.
The Manufacturing Process: An Eco-Friendly Approach
The production of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics is relatively efficient and involves a lower energy consumption compared to traditional woven textiles. The manufacturing process includes:
1. **Polymer Production**: Polypropylene is derived from propylene gas, which is a byproduct of oil refining, making it accessible and cost-effective.
2. **Fiber Formation**: The polymer is melted and extruded into thin fibers, which can then be laid down in various configurations, such as spunbond or meltblown.
3. **Bonding Techniques**: The fibers are bonded together using heat, pressure, or adhesives, resulting in a fabric that is durable yet lightweight.
This streamlined process not only conserves energy but also minimizes waste, reinforcing the sustainable nature of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics.
Key Environmental Benefits of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics offer several environmental advantages that contribute to their growing popularity. The following sections highlight their key benefits.
1. Biodegradability and Recyclability
One of the significant environmental benefits of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics is their recyclability. Unlike many synthetic materials, polypropylene can be effectively recycled and repurposed, reducing landfill waste. The recycling process generally involves:
- Gathering used polypropylene products.
- Cleaning and processing them into pellets.
- Creating new polypropylene products from these pellets.
In addition, while polypropylene is not biodegradable, it can degrade more rapidly than other plastics under certain conditions, depending on environmental factors. This characteristic reduces its long-term impact on the ecosystem when properly managed.
2. Reduced Resource Consumption
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics require significantly fewer natural resources compared to traditional woven fabrics. The water consumption in the production of these materials is minimal, which is especially crucial in regions facing water scarcity. Additionally, the energy requirements for producing polypropylene are lower than those for cotton or polyester, making it an efficient choice in terms of resource utilization.
3. Lightweight and Durable
The lightweight nature of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics leads to lower transportation costs and reduced energy consumption during shipping. Their durability means they can withstand harsh conditions, resulting in less frequent replacements and less waste over time. This longevity contributes positively to overall resource conservation.
4. Versatile Applications
The versatility of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics enables their use in various eco-friendly applications. They can be found in:
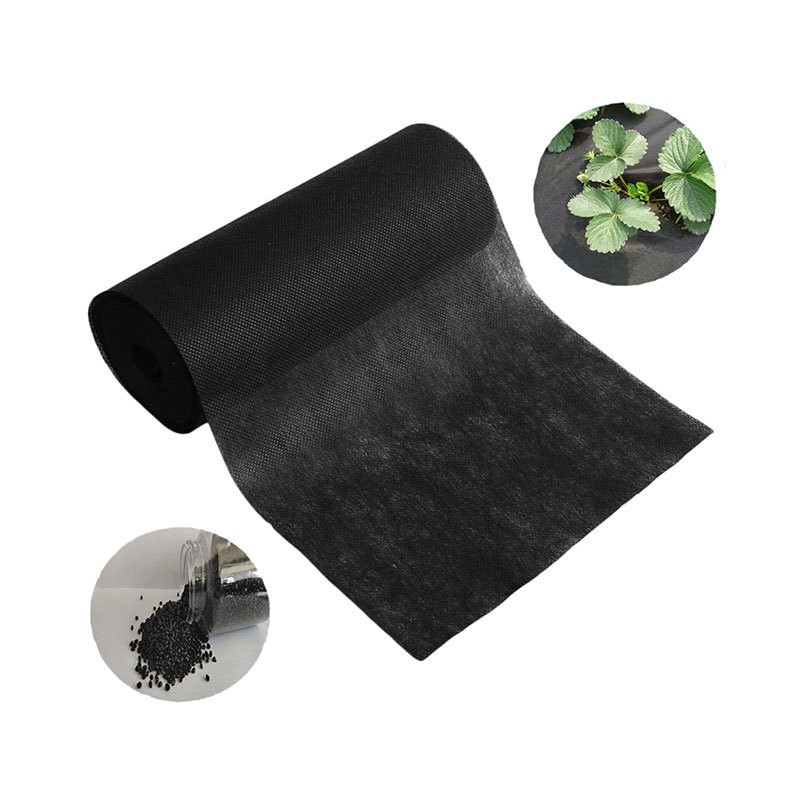
- **Agriculture**: Used as mulch, weed barriers, and protective covers, they promote sustainable farming practices.
- **Medical Supplies**: In personal protective equipment (PPE), they offer safety while minimizing environmental impact.
- **Home Textiles**: From geotextiles to furniture upholstery, these materials provide eco-conscious options for consumers.
Each application underscores the adaptability of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, making them an attractive choice for diverse industries.
5. Contribution to Circular Economy
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics play a crucial role in promoting a circular economy. By being recyclable, they fit within a framework that emphasizes sustainability by keeping materials in use for longer and minimizing waste. The ability to recycle and repurpose materials means that industries can source new products from existing ones, thereby reducing the need for virgin materials.
Comparing Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics with Other Materials
To understand the environmental benefits of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics fully, it is essential to compare them with other commonly used materials.
Polyester vs. Polypropylene
Polyester is another popular synthetic fabric but has a more significant environmental footprint due to its petroleum-based origins and energy-intensive production process. While both materials are recyclable, polypropylene has a lower energy requirement during production, making it a more sustainable choice.
Cotton vs. Polypropylene
Cotton is often hailed as a natural and biodegradable option; however, its cultivation requires vast amounts of water and pesticides, contributing to environmental degradation. In contrast, polypropylene nonwoven fabrics provide a more sustainable solution without the high resource consumption associated with cotton farming.
Biodegradable Alternatives
While biodegradable fabrics like hemp or organic cotton appear to offer eco-friendly options, they may not provide the same durability and versatility as polypropylene nonwoven fabrics. The latter can serve multiple functions without the environmental costs associated with their production.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Adoption of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
Despite the numerous environmental benefits, the adoption of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics faces challenges.
1. Public Perception and Awareness
Consumer awareness regarding the benefits of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics is crucial. Many people remain uninformed about their sustainability, leading to misconceptions about synthetic materials. Increased education and outreach can help shift public perception.
2. Recycling Infrastructure
While polypropylene is recyclable, the infrastructure for recycling such materials is still developing in many regions. Improving recycling facilities and processes will enhance the effectiveness of polypropylene nonwoven fabric recycling.
3. Innovations in Production
Investing in research and development can lead to innovations in the production of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, further enhancing their eco-friendliness. Advances in technology can reduce energy consumption and improve recyclability.
Future Prospects: The Role of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics in Sustainability
As more industries recognize the importance of sustainability, the demand for eco-friendly materials like polypropylene nonwoven fabrics will continue to grow. We anticipate several trends shaping the future:
1. Increased Usage in Eco-Conscious Products
With consumers increasingly seeking sustainable products, industries will likely incorporate polypropylene nonwoven fabrics into their offerings, promoting eco-friendly choices.
2. Developments in Recycling Techniques
Advancements in recycling technology will make the recycling process for polypropylene more efficient, encouraging greater adoption of these fabrics.
3. Greater Regulatory Support
Governments may implement policies promoting sustainable materials, driving industries to adopt polypropylene nonwoven fabrics as part of their commitment to environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are polypropylene nonwoven fabrics made from?
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are made from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer that is lightweight and durable. The manufacturing process involves melting and extruding the polymer into fibers, which are then bonded together.
2. Are polypropylene nonwoven fabrics biodegradable?
While polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are not biodegradable, they can be recycled, which reduces their environmental impact. They can break down more rapidly than other plastics under certain conditions.
3. How do polypropylene nonwoven fabrics compare to cotton?
Cotton requires significant water and pesticides for cultivation, making it less sustainable than polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, which consume fewer resources during production.
4. What are the main applications of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics?
These fabrics are widely used in agriculture, medical supplies, home textiles, and more, thanks to their versatility and eco-friendliness.
5. How can consumers contribute to the sustainability of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics?
Consumers can support sustainability by choosing products made from polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, recycling them when possible, and advocating for greater awareness and infrastructure for recycling.
Conclusion
The environmental benefits of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics present a compelling case for their use across various industries. From their recyclability and reduced resource consumption to their versatile applications, these materials align with the growing global movement towards sustainability. As we move forward, embracing polypropylene nonwoven fabrics can significantly contribute to a greener future, making them a pivotal choice for eco-conscious consumers and industries alike.
nonwoven fabric polypropylene