27
2025
-
06
Sustainability in Textiles: The Role of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Sustainability in Textiles: The Role of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Sustainability in Textiles 2. The Importance of Sustainability in the Textile Industry 3. What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric? 4. Benefits of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric 5. Applications of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric in Textiles 6. Environmental Impact of PP Spunbond Nonwoven F
Sustainability in Textiles: The Role of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Sustainability in Textiles
- 2. The Importance of Sustainability in the Textile Industry
- 3. What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric?
- 4. Benefits of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
- 5. Applications of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric in Textiles
- 6. Environmental Impact of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
- 7. Innovations and Future Trends in Nonwoven Textiles
- 8. Challenges and Solutions in Sustainable Textile Production
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction to Sustainability in Textiles
In today's world, the textile industry is undergoing a significant transformation towards sustainability. As environmental concerns rise, consumers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products. This shift compels manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices and materials. One of the leading innovations in this area is **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric**. This article delves into the critical role this material plays in promoting sustainability within the textile sector.
2. The Importance of Sustainability in the Textile Industry
Sustainability in textiles addresses the ecological, social, and economic impacts of textile production. The industry notoriously contributes to pollution, excessive waste, and resource depletion. By implementing sustainable practices, the textile industry can reduce its environmental footprint, promote ethical practices, and create durable products that meet consumer needs.
Some essential aspects of sustainability in textiles include:
- **Resource Efficiency:** Minimizing water and energy consumption during production processes.
- **Waste Reduction:** Developing recycling and upcycling strategies for textile waste.
- **Eco-Friendly Materials:** Utilizing biodegradable and renewable resources in textile manufacturing.
- **Ethical Labor Practices:** Ensuring fair treatment of workers throughout the supply chain.
3. What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric?
**PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** is a type of fabric made from polypropylene fibers. The production process involves melting polypropylene pellets and extruding them into continuous filaments, which are then laid down and bonded through thermal or mechanical means. This innovative fabric is characterized by its lightweight, strength, and versatility, making it suitable for various applications in textiles.
Key features of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric include:
- **High Strength:** The fabric boasts superior tensile strength, making it durable and long-lasting.
- **Breathability:** Its structure allows airflow, which is essential in applications like hygiene products.
- **Chemical Resistance:** This fabric is resistant to various chemicals, enhancing its usability in different environments.
- **Cost-Effectiveness:** The manufacturing process is efficient, resulting in lower production costs compared to traditional woven fabrics.
4. Benefits of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Adopting **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** offers numerous benefits that align with sustainable practices in the textile industry. Some of these benefits include:
4.1 Eco-Friendly Production
The production of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric requires significantly less water compared to conventional textiles. This reduction in water usage is vital, especially in regions facing water scarcity. Additionally, the fabric can be produced without harmful chemicals, minimizing environmental pollution.
4.2 Recyclability and Biodegradability
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is recyclable, allowing manufacturers and consumers to participate in a circular economy. When disposed of properly, it can be recycled into new products, reducing landfill waste. Furthermore, advancements in biodegradable options for PP spunbond are emerging, further enhancing its eco-friendliness.
4.3 Versatility in Applications
This fabric can be utilized across various sectors, including fashion, hygiene, medical, and home textiles. Its adaptability allows designers and manufacturers to create innovative products that meet consumer demands while adhering to sustainability principles.
5. Applications of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric in Textiles
The versatility of **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** enables its use in diverse applications, contributing to sustainable solutions across various industries.
5.1 Hygiene Products
One of the most significant uses of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is in hygiene products, such as diapers, feminine hygiene items, and medical gowns. The breathable and soft texture ensures comfort while providing protection against leaks.
5.2 Fashion and Apparel
Sustainable fashion is on the rise, and PP spunbond is increasingly being incorporated into clothing and accessories. Designers utilize this fabric to create lightweight, stylish, and functional garments that are also eco-friendly.
5.3 Home Textiles
From curtains to upholstery, PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is finding its way into home textiles. Its durability and ease of maintenance make it an ideal choice for various household applications.
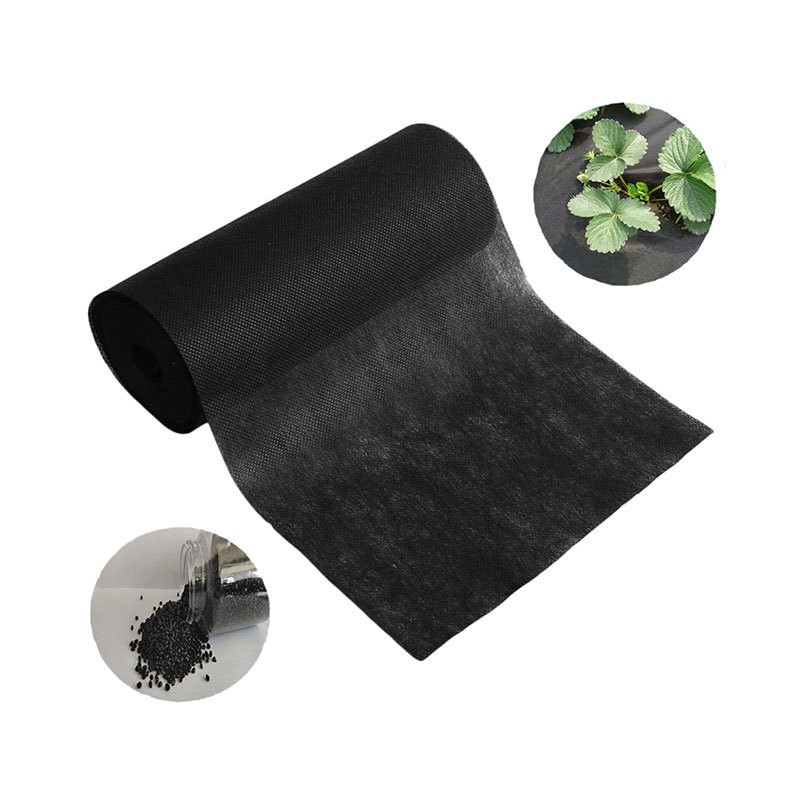
5.4 Industrial Applications
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is widely used in the automotive and construction industries for applications like insulation, filtration, and protective covers. Its robustness and chemical resistance make it suitable for demanding environments.
6. Environmental Impact of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Examining the environmental impact of **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** reveals a mixture of advantages and challenges. While the fabric itself is associated with several eco-friendly characteristics, understanding its overall lifecycle is crucial for assessing sustainability.
6.1 Carbon Footprint Analysis
The carbon footprint of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is generally lower than that of traditional textiles. However, it is essential to consider the entire production process, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, and transportation, to accurately evaluate its environmental impact.
6.2 End-of-Life Management
Effective end-of-life management is critical for minimizing waste. As recycling infrastructures develop, the potential for repurposing PP spunbond nonwoven fabric increases, presenting a sustainable alternative to disposal in landfills.
7. Innovations and Future Trends in Nonwoven Textiles
The future of **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** is bright, with ongoing innovations aiming to enhance its sustainability profile. Emerging trends include:
7.1 Smart Textiles
The integration of smart technology into nonwoven fabrics is gaining traction. This includes the development of textiles that can monitor environmental conditions or respond to external stimuli, adding value beyond traditional uses.
7.2 Biodegradable Alternatives
Research is underway to create biodegradable nonwoven fabrics from renewable sources, such as plant-based polymers. These alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact further and align with sustainability goals.
7.3 Enhanced Recycling Processes
Advancements in recycling technologies are expected to improve the efficiency of processing PP spunbond nonwoven fabric, making end-of-life management easier and more effective.
8. Challenges and Solutions in Sustainable Textile Production
Despite the benefits of **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric**, challenges remain in achieving full sustainability within the textile industry.
8.1 Overcoming Consumer Perception
A significant challenge is changing consumer perception regarding nonwoven fabrics. Educating consumers on the benefits of sustainability and the innovative qualities of PP spunbond fabric is essential.
8.2 Addressing Supply Chain Issues
Ensuring that sustainability principles are applied throughout the supply chain can be complex. Collaborating with suppliers and implement rigorous standards and certifications can lead to more sustainable practices.
9. Conclusion
As the textile industry continues to evolve toward sustainability, **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** stands out as a key player in this transformative journey. Its eco-friendly properties, diverse applications, and potential for innovation position it as a sustainable alternative to traditional textiles. By embracing this material, manufacturers, designers, and consumers can contribute to a more sustainable future while meeting the demand for high-quality products. Through collaboration and commitment to sustainable practices, the textile industry can effectively address environmental challenges while fostering innovation and growth.
10. FAQs
What is PP spunbond nonwoven fabric made of?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is primarily made from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer.
Is PP spunbond nonwoven fabric biodegradable?
Traditional PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is not biodegradable; however, there are ongoing developments aimed at creating biodegradable alternatives.
What industries use PP spunbond nonwoven fabric?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is utilized in various industries, including hygiene, fashion, automotive, and home textiles.
How does PP spunbond compare to traditional woven fabrics?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric generally offers greater strength, lighter weight, and lower production costs compared to traditional woven fabrics.
Can PP spunbond nonwoven fabric be recycled?
Yes, PP spunbond nonwoven fabric can be recycled, contributing to a circular economy and reducing landfill waste.
pp spunbond nonwoven fabric