10
2025
-
08
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabric: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabric Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics 2. What is Polypropylene? 3. Benefits of Nonwoven Fabrics 4. Overview of the Manufacturing Process 5. Raw Materials Used in Production 6. Key Production Methods 6.1 Spunbond Process 6.2 Meltblown Proce
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabric
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
- 2. What is Polypropylene?
- 3. Benefits of Nonwoven Fabrics
- 4. Overview of the Manufacturing Process
- 5. Raw Materials Used in Production
- 6. Key Production Methods
- 7. Quality Control Measures
- 8. Applications of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
- 9. Future Trends in Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing
- 10. Conclusion
- 11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
In the modern textile industry, **polypropylene nonwoven fabric** has emerged as a key player. This innovative material is distinguished by its unique properties and versatile applications. As industries increasingly seek efficient and cost-effective solutions, understanding the manufacturing process of polypropylene nonwoven fabric becomes essential. This guide elucidates the various stages involved in the production of this fabric, highlighting its benefits and future trends.
2. What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in a variety of applications due to its durability, resistance to chemical solvents, and low density. It is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic globally. In the context of nonwoven fabrics, polypropylene is favored for its lightweight nature and ability to be engineered into a myriad of textures and finishes. The versatility of polypropylene allows it to be used in everything from medical supplies to automotive interiors.
3. Benefits of Nonwoven Fabrics
Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics offer a plethora of benefits that contribute to their popularity in multiple sectors. These include:
- **Lightweight yet Strong**: Despite their low weight, nonwoven fabrics possess remarkable tensile strength, making them suitable for various applications.
- **Breathable and Moisture-Wicking**: Polypropylene allows air and moisture to pass through, which is particularly advantageous for products like hygiene and medical textiles.
- **Cost-Effectiveness**: The manufacturing process is generally less expensive than traditional woven fabrics, leading to lower production costs.
- **Eco-Friendly Options**: With a growing focus on sustainability, many manufacturers are adopting biodegradable materials or recycling post-consumer polypropylene for fabric production.
- **Customizable Properties**: The properties of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics can be tailored for specific applications, including UV resistance, flame retardance, and antimicrobial finishes.
4. Overview of the Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of polypropylene nonwoven fabric can be segmented into several key stages:
1. **Raw Material Preparation**: The process begins with selecting high-quality polypropylene pellets.
2. **Polymerization**: The polypropylene is melted and extruded into fibers.
3. **Web Formation**: The fibers are laid down in a web-like structure, either through spinning or blowing methods.
4. **Bonding**: The web is then bonded together using various techniques such as heat, chemical, or mechanical bonding.
5. **Finishing**: Finally, the fabric undergoes finishing treatments to enhance its properties and prepare it for use in different applications.
Each stage plays a crucial role in determining the final characteristics of the nonwoven fabric.
5. Raw Materials Used in Production
The primary raw material for manufacturing polypropylene nonwoven fabric is polypropylene resin. The quality of the resin significantly impacts the final product's performance. Additional materials may include:
- **Additives**: These can enhance certain properties, such as UV stability or flame resistance.
- **Colorants**: Dyes and pigments can be added during the manufacturing process to achieve desired colors.
- **Recycled Materials**: A growing number of manufacturers are incorporating recycled polypropylene to minimize environmental impact.
Selecting the right combination of raw materials is essential for producing high-quality nonwoven fabrics.
6. Key Production Methods
The production of polypropylene nonwoven fabric primarily employs three methods: spunbond, meltblown, and other specialized techniques.
6.1 Spunbond Process
The **spunbond** method involves extruding molten polypropylene through spinnerets to form continuous filaments. These filaments are cooled and laid out on a conveyor belt to form a web. The web is then bonded through various methods, creating a strong fabric that is widely used for applications such as hygiene products, medical textiles, and geotextiles.
6.2 Meltblown Process
In the **meltblown** process, polypropylene is again melted and extruded, but the filaments are blown by hot air to create extremely fine fibers. This process results in a fabric that is soft, absorbent, and effective for filtration applications. Meltblown polypropylene is commonly used in face masks, surgical gowns, and other healthcare-related products.
6.3 Other Production Techniques
While spunbond and meltblown are the two primary methods, several other techniques exist, such as:
- **Needle Punching**: This method uses barbed needles to entangle fibers, adding strength to the fabric.
- **Hydroentangling**: High-pressure water jets are used to bond fibers together, resulting in softer fabrics suitable for medical and hygiene applications.
Each method offers unique advantages and meets specific industry requirements.
7. Quality Control Measures
Ensuring the quality of polypropylene nonwoven fabric is paramount. Several quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process:
- **Material Inspection**: Raw materials are rigorously tested for purity and consistency.
- **Process Monitoring**: Continuous monitoring of parameters such as temperature and pressure during production ensures optimal conditions.
- **Final Product Testing**: Finished fabrics undergo various tests, including tensile strength, thickness measurements, and absorbency tests, to ensure they meet specified standards.
By adhering to strict quality control protocols, manufacturers can consistently deliver high-quality polypropylene nonwoven fabrics.
8. Applications of Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics
The versatility of polypropylene nonwoven fabrics allows them to be used across a range of industries, including:
- **Medical and Hygiene**: This includes surgical masks, gowns, and diapers, where the fabric's absorbency and breathability are crucial.
- **Automotive**: Polypropylene nonwoven fabrics are used in car interiors, providing insulation, sound dampening, and aesthetic appeal.
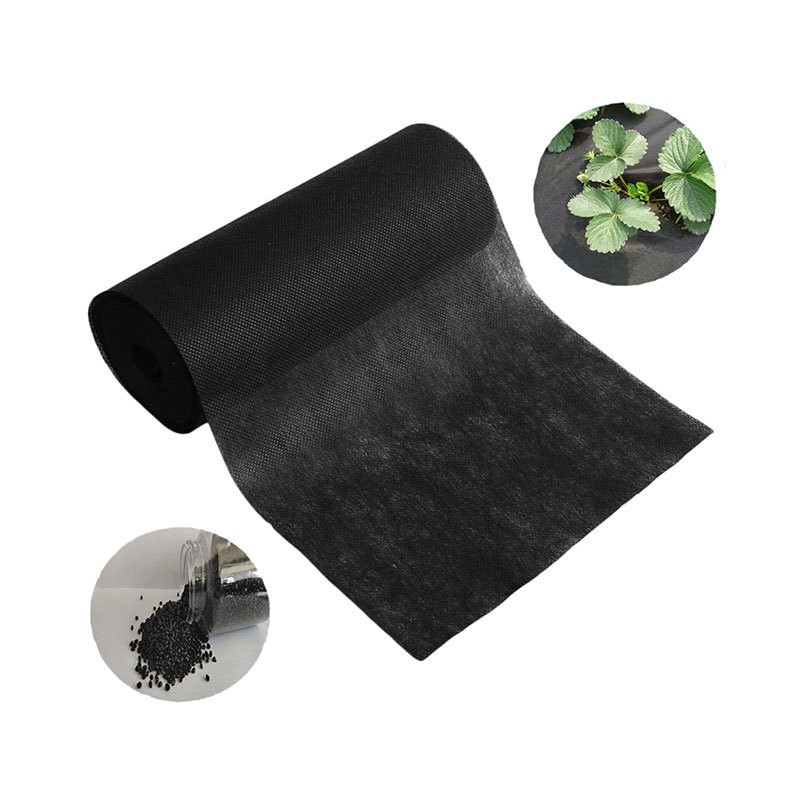
- **Construction**: Geotextiles made from polypropylene are essential for soil stabilization and erosion control.
- **Home Textiles**: Products like disposable tablecloths, shopping bags, and upholstery materials benefit from the durability and ease of maintenance of nonwoven fabrics.
As technology advances, new applications for polypropylene nonwoven fabrics continue to emerge.
9. Future Trends in Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing
The nonwoven fabric industry is poised for significant advancements in the coming years. Key trends include:
- **Sustainability**: The shift towards eco-friendly materials and processes is gaining momentum, with many manufacturers focusing on biodegradable and recyclable options.
- **Technological Innovations**: Advances in manufacturing technology, such as automation and Industry 4.0, are improving efficiency and product quality.
- **Customization**: Increasing demand for specialized fabrics tailored to specific applications will drive innovation in production techniques and raw materials.
Staying abreast of these trends will be vital for manufacturers looking to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
10. Conclusion
The manufacturing process of polypropylene nonwoven fabric is a complex yet fascinating journey that combines advanced technology with creative engineering. From the selection of raw materials to the application of quality controls, every step is crucial in producing a versatile and high-quality product. As industries continue to recognize the advantages of nonwoven fabrics, the demand for polypropylene options is likely to grow, fostering innovation and sustainability in the textile sector.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is polypropylene nonwoven fabric used for?
Polypropylene nonwoven fabric is used in various applications including medical supplies, automotive interiors, construction materials, and home textiles.
How is polypropylene nonwoven fabric made?
The fabrication process involves melting polypropylene pellets, extruding them into fibers, forming a web, bonding the fibers, and finishing the fabric.
What are the advantages of using nonwoven fabrics?
Nonwoven fabrics offer benefits such as lightweight strength, breathability, cost-effectiveness, and customizable properties.
Is polypropylene nonwoven fabric eco-friendly?
Many manufacturers are now creating biodegradable and recyclable polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, contributing to more sustainable practices.
What are the main production methods for nonwoven fabrics?
The primary production methods include spunbond, meltblown, needle punching, and hydroentangling.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip readers with an in-depth understanding of the manufacturing process of polypropylene nonwoven fabric, its benefits, and its applications, catering to both industry professionals and those interested in textile innovations.
nonwoven fabric polypropylene