26
2025
-
08
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric Table of Contents Introduction to PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric? Raw Materials Used in Production The Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process 1. Polymerization 2. Fiber Formation 3. Web Formation 4. Bonding Techniques
Understanding the Manufacturing Process of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
Table of Contents
- Introduction to PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
- What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric?
- Raw Materials Used in Production
- The Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
- Quality Control Measures
- Applications of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
- Advantages of Using PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction to PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
The textile industry has undergone significant advancements in recent years, with nonwoven fabrics emerging as a key player in various applications. Among these, **PP spunbond nonwoven fabric** has gained immense popularity due to its unique properties and versatility. This article delves into the manufacturing process of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric, providing insights into its production, quality control, and applications.
What is PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is a type of fabric made from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer. Unlike traditional woven fabrics, nonwoven fabrics are manufactured by bonding or interlocking fibers through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes. This results in a material that is lightweight, durable, and resistant to tearing, making it an ideal choice for various applications, including medical supplies, hygiene products, and geotextiles.
Raw Materials Used in Production
The production of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric relies on high-quality raw materials to ensure optimal performance and durability. The primary raw material is polypropylene resin, which is processed to create fibers. Other additives may include:
- **Colorants**: To achieve desired colors.
- **UV Stabilizers**: To enhance resistance to sunlight.
- **Antimicrobial Agents**: For hygiene applications.
The careful selection of these materials plays a crucial role in the overall quality of the final product.
The Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric consists of several key steps, each contributing to the final product's quality and characteristics.
1. Polymerization
The first step in the manufacturing process is **polymerization**, where polypropylene pellets are melted and extruded into a continuous filament. This process takes place in an industrial extruder, which heats the pellets to a specific temperature, allowing them to flow and form a molten mass.
2. Fiber Formation
Once the polypropylene is in a molten state, it is forced through spinnerets—devices with numerous tiny holes that shape the molten polymer into continuous filaments. As these filaments exit the spinneret, they are cooled and solidified in the air, forming individual fibers.
3. Web Formation
The next step involves **web formation**, where the continuous filaments are laid down to create a web-like structure. This can be achieved using various methods, such as:
- **Cross-lapping**: The fibers are layered in a crisscross pattern.
- **Air-laying**: The fibers are suspended in air and then directed to form a web.
The method chosen will influence the final texture and density of the fabric.
4. Bonding Techniques
The final step in the manufacturing process is **bonding**, where the web of fibers is stabilized. This can be done using several techniques, including:
- **Thermal bonding**: Heat is applied to melt specific areas of the fibers, causing them to bond together.
- **Chemical bonding**: A bonding agent is applied to create a cohesive fabric.
- **Mechanical bonding**: Needling or stitching techniques are used to entangle the fibers.
Each bonding technique provides unique properties to the nonwoven fabric, affecting its strength, flexibility, and intended use.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount in the production of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric. Manufacturers implement rigorous testing procedures to ensure that the fabric meets industry standards and specifications. Key quality control measures include:
- **Tensile Strength Testing**: To assess the fabric's durability.
- **Weight Per Unit Area Measurement**: To ensure consistent thickness.
- **Tear Resistance Testing**: To evaluate how well the fabric withstands stress.
- **Color Fastness Testing**: To confirm that colors remain stable over time.
By adhering to strict quality control protocols, manufacturers can guarantee the reliability and performance of their PP spunbond nonwoven fabrics.
Applications of PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is incredibly versatile and finds applications in numerous industries, including:
- **Medical and Hygiene Products**: Used in surgical gowns, masks, and diapers due to its breathable and liquid-repellent properties.
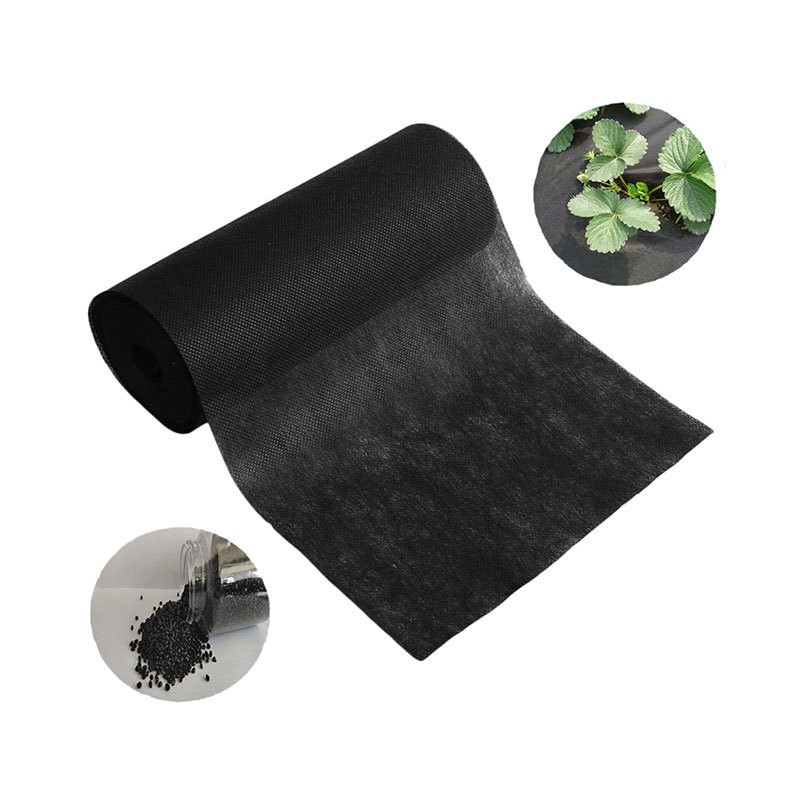
- **Agriculture**: Employed as mulch films and plant covers to enhance growth and protect crops.
- **Geotextiles**: Utilized for soil stabilization and erosion control.
- **Automotive**: Applied in interior components for lightweight and durable solutions.
- **Home Furnishings**: Used in upholstery and other textile applications.
The diverse applications highlight the fabric's adaptability and importance in modern manufacturing.
Advantages of Using PP Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
The popularity of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric can be attributed to its numerous advantages, including:
- **Cost-Effectiveness**: The manufacturing process is efficient, resulting in lower production costs.
- **Lightweight**: The fabric is easy to handle and transport, reducing shipping expenses.
- **Breathability**: It allows air and moisture to pass through, making it suitable for various applications.
- **Durability**: PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is strong and resistant to tearing, ensuring longevity.
These benefits make it a preferred choice for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is a complex yet fascinating journey that involves careful planning, quality materials, and precise techniques. Understanding this process not only highlights the fabric's versatility but also underscores its significance in numerous applications across industries. As we continue to innovate and improve manufacturing practices, the future of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric looks promising, paving the way for new and exciting uses.
FAQs
1. What is PP spunbond nonwoven fabric made from?
PP spunbond nonwoven fabric is primarily made from polypropylene, a type of thermoplastic polymer.
2. What are the main advantages of using PP spunbond nonwoven fabric?
The main advantages include cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, breathability, and durability.
3. In what industries is PP spunbond nonwoven fabric commonly used?
It is commonly used in medical, agricultural, automotive, and home furnishing industries.
4. How is the quality of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric ensured?
Quality is ensured through rigorous testing, including tensile strength, weight, tear resistance, and color fastness testing.
5. What bonding techniques are used in the manufacturing process?
Common bonding techniques include thermal bonding, chemical bonding, and mechanical bonding.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth understanding of the manufacturing process of PP spunbond nonwoven fabric, its applications, and the benefits it offers. As the demand for innovative and high-quality materials grows, so does the importance of understanding the processes that create them.
pp spunbond nonwoven fabric